MOLECULAR ELECTRONICS
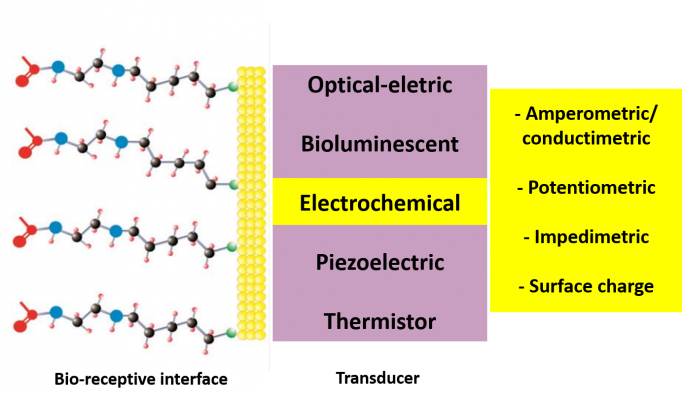
Within the context of mimetics, the Nanobionics group has created strategies to study biomolecular affinity and molecular binding kinetics in a chip – termed as a biosensor. The electrochemical biosensor’s interface is highly selective and able to detect an analyte of interest by the combination of a biological receptor component and a physicochemical transducer. Electrochemical biosensors use electrochemical concepts as transducer signals to convert a biological reaction or a binding event into a measurable and quantifiable electronic signal. By immobilizing a biological molecule, such as a marker antibody for a particular disease on the surface of the microelectrodes designed at the molecular level, it is possible to detect, for example, the presence of its antigen in a blood sample by means of quantum capacitive methods: any electrical signal different from the reference signal can be identified and quantified, allowing, for example, the early diagnosis of different diseases. Indeed the quantification of biological or biochemical processes is of utmost importance for medical, biological and biotechnological applications.
The general performance of electrochemical biosensor devices is often a combination of the surface architectures (that connects the sensing element to the biological sample at the nanometer scale) with the transduction signal used. Electrochemical biosensors based on potentiometric principles monitor changes on the electrode potential caused by any biological event occurring on the biosensor’s interface that modifies the equilibrium of the redox reaction. Amperometric biosensors are relatively sensitive and operate based on the measurement of the direct current (DC) current or current density associated with an electrochemistry reaction occurring in the biosensor’s surface usually due to the application of an electrochemical potential difference between the current collector and the counter electrode. Impedimetric biosensors are based on the electrochemical impedance measurement which is indeed related to the opposition that an electronic circuit presents to a current when a small perturbative oscillatory voltage is applied on the interface (electrical impedance).